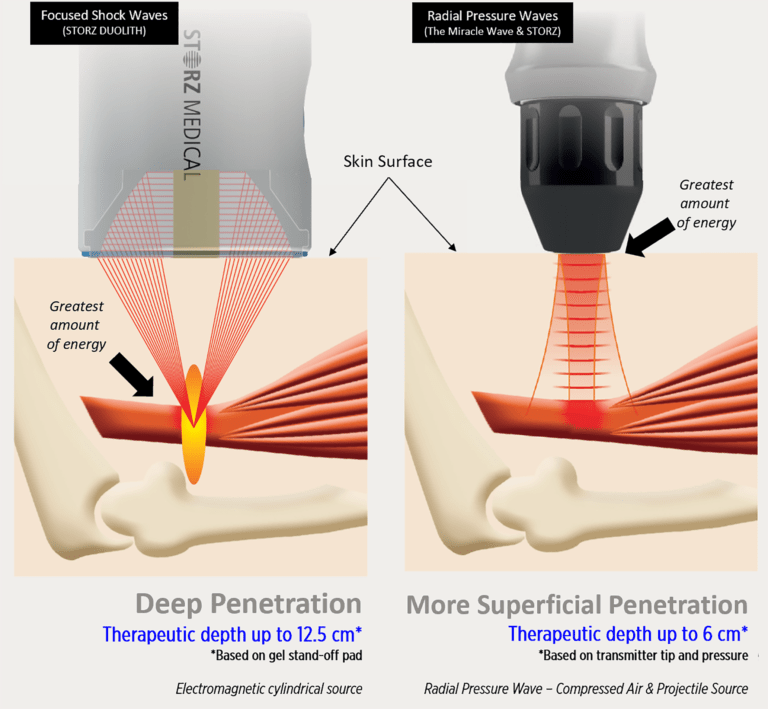
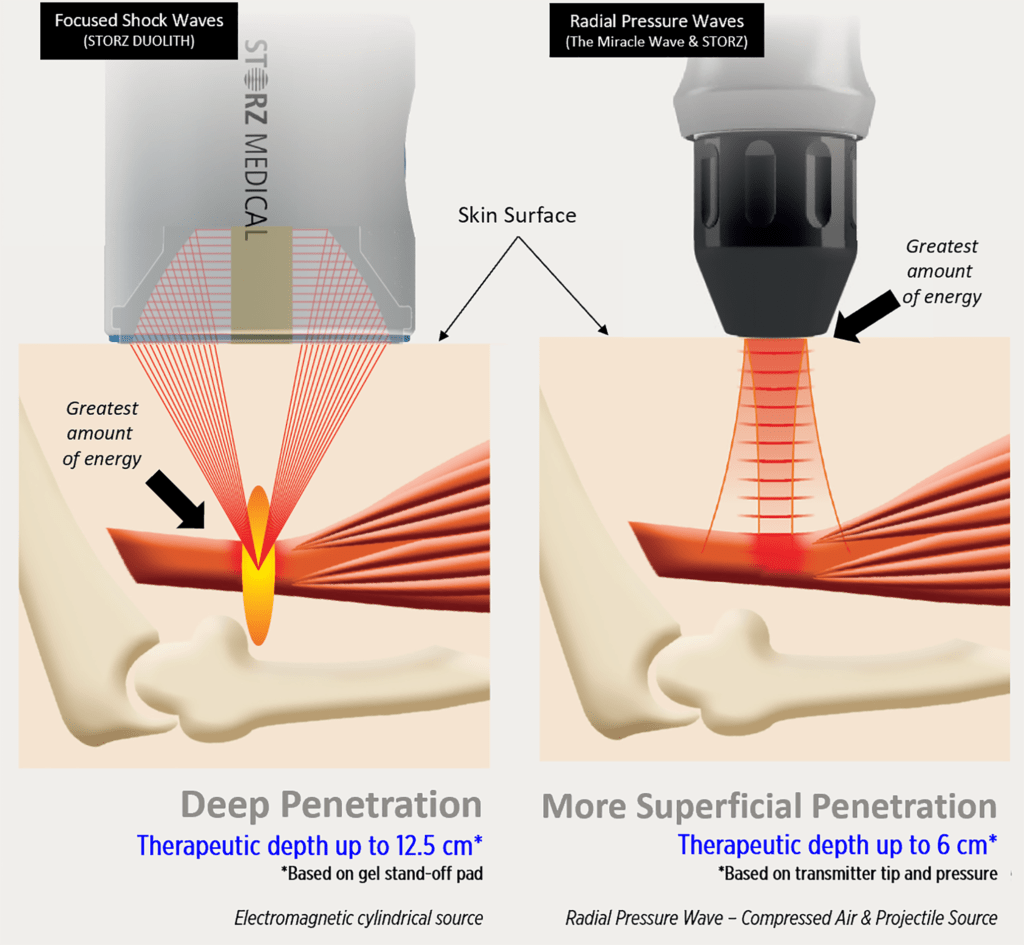
In musculoskeletal (MSK) therapy, the technology continues to evolve, offering patients new treatment options for conditions ranging from tendonitis to chronic pain. Two prominent therapies that have gained attention in recent years are Radial Pressure Wave Therapy (rESWT) and Focused Shockwave Therapy (FST), both referred to as shockwave therapy or acoustic wave therapy. While both leverage shockwave technology to achieve excellent results, they differ significantly in how they are produced, as well as their therapeutic effectiveness zones. Let’s delve into the distinctions between these two treatments to better understand their respective benefits and applications.
Radial Pressure Wave Therapy (rESWT)
Radial Pressure Wave Therapy, also known as Acoustic Wave Therapy, utilizes a handheld device that emits low-energy acoustic waves using a ballistics system. These waves are transmitted radially, meaning they spread out from a central point and target a broader area of tissue. The key characteristics of Radial Pressure Wave include:
- Mechanism of Action: rESWT generates kinetic energy that is transmitted through the skin and into the tissues. This energy promotes increased blood circulation, stimulates cellular metabolism, and facilitates the dissolution of calcifications or fibrosis.
- Treatment Area: It is particularly effective for treating larger, more superficial areas of tissue, such as the muscles and tendons. Radial pressure wave is commonly used for conditions like muscle strains, tendinopathies (e.g., Achilles tendonitis), and trigger points.
- Patient Experience: Radial Pressure Wave Therapy typically involves a series of sessions spaced over several weeks. The treatment itself is generally well-tolerated, causing mild discomfort at most, and does not require anesthesia or downtime.
Focused Shockwave Therapy (fESWT)
Focused Shockwave Therapy, on the other hand, involves a device that emits shockwaves focused on a precise point within the body. These shockwaves are high-energy sound waves that travel faster than the speed of sound and are capable of penetrating deeper into tissues. The distinguishing features of FST include:
- Mechanism of Action: FST delivers shockwaves directly to a targeted area, such as a specific tendon insertion or a chronic injury site. This focused energy induces controlled microtrauma, which stimulates healing processes, promotes tissue regeneration, and reduces inflammation.
- Treatment Area: It is particularly suited for treating localized musculoskeletal issues that require precise targeting, such as plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis), and calcific shoulder tendinitis.
- Patient Experience: FST sessions are typically shorter in duration compared to RPWT, and fewer sessions may be required overall. The therapy may cause mild discomfort during treatment, and some patients might experience temporary soreness afterward.
Choosing the Right Therapy
When considering RPWT vs. FST for MSK conditions, several factors come into play:
- Condition Type: The nature and location of the musculoskeletal condition will influence which therapy is more suitable. RPWT is advantageous for larger areas or more diffuse issues, while FST excels in targeting specific anatomical sites.
- Treatment Goals: The desired therapeutic outcome, whether it’s pain relief, tissue repair, or functional improvement, should guide therapy selection.
- Patient Preferences: Individual preferences regarding treatment duration, intensity, and potential discomfort should be taken into account to optimize patient compliance and satisfaction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while Radial Pressure Wave Therapy (RPWT) and Focused Shockwave Therapy (FST) both harness the power of shockwaves for musculoskeletal treatment, their methods of delivery and therapeutic targets differ significantly. RPWT offers a broader, more diffuse treatment for larger areas of tissue, promoting circulation and metabolic activity. In contrast, FST provides targeted, high-energy shockwaves to precise anatomical locations, inducing controlled microtrauma and promoting tissue healing. The choice between these therapies depends on the specific condition being treated, the desired therapeutic outcomes, and patient preferences. Consulting with a healthcare provider who specializes in MSK conditions can help determine the most appropriate treatment approach for individual needs.