Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is known for treating musculoskeletal conditions and kidney stones, but emerging research is exploring its use in nervous system diseases. Studies suggest ESWT shows promise in managing conditions such as neuropathic pain, spasticity, and even neurodegenerative diseases.
What is ESWT and How Does It Work?
ESWT uses high-energy sound waves targeted at specific areas of the body. These waves stimulate mechanical and biochemical effects that aid tissue healing and regeneration. There are two types of shockwaves:
- Focused Shockwave Therapy (FSWT): Delivers high-energy waves to a localized area at greater penetration depths.
- Radial Shockwave Therapy (RSWT): Distributes lower energy waves over a wider area at a more superficial depth.
In nervous system applications, ESWT is thought to promote:
- Neuroplasticity and Nerve Regeneration: It may enhance the brain’s ability to form new neural connections by boosting nerve growth factors like Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF).
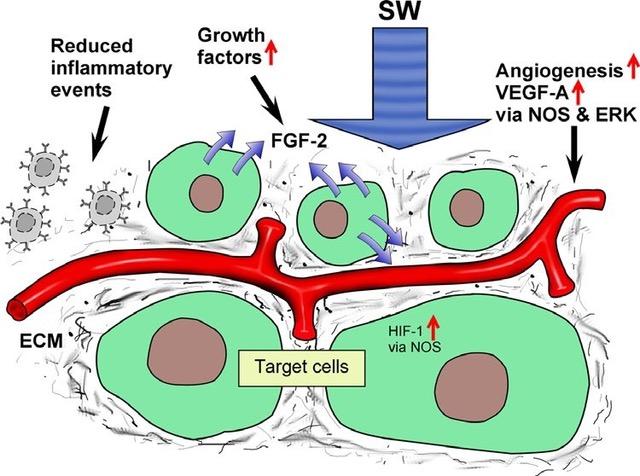
- Inflammation Modulation: ESWT reduces inflammation in nerve tissues by downregulating pro-inflammatory molecules and promoting anti-inflammatory mediators.
- Blood Flow Improvement: It enhances blood flow by promoting new blood vessel formation (angiogenesis), improving oxygen and nutrient supply to damaged nerves.
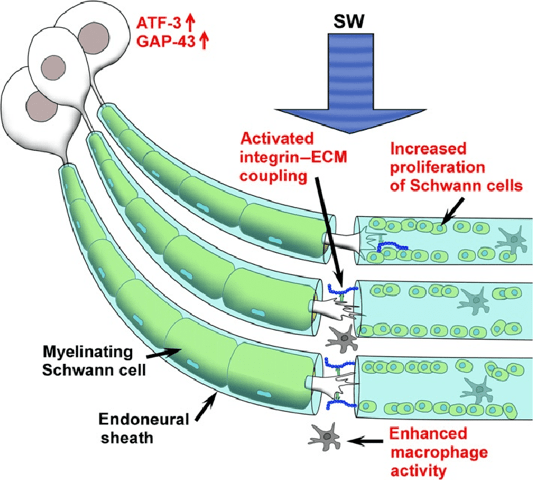
How Is ESWT Applied to Nervous System Diseases?
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Peripheral neuropathy, which causes pain and numbness due to nerve damage, may benefit from ESWT. Studies have shown that low-intensity ESWT can alleviate symptoms by promoting nerve regeneration and reducing oxidative stress.
- Post-Stroke Spasticity: After a stroke, many patients experience spasticity (muscle stiffness). Research has demonstrated that ESWT can reduce muscle hyperactivity and improve motor function by influencing neuromuscular transmission.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Though still in early stages, studies suggest ESWT may help improve motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease by stimulating neural pathways and enhancing neuroplasticity, with potential applications for other neurodegenerative conditions as well.
- Neuropathic Pain Management: ESWT has shown effectiveness in managing chronic nerve-related pain, such as in conditions involving nerve root compression. It can offer pain relief when traditional treatments are inadequate.
What Are the Advantages and Considerations of ESWT for Nervous System Conditions?
Advantages:
- Non-Invasive: ESWT is a non-surgical treatment option with positive patient outcomes worldwide.
- Minimal Side Effects: When administered properly, it has little to no side effects. No downtime!
- Reduced Medication Use: It may help reduce the need for pain medications, including opioids.
- Highly Researched: Shockwave Therapy is one of the largest researched non-invasive technologies in the world!
Considerations:
- Treatment Protocols: The best parameters (energy levels, frequency, number of sessions) for treating specific nervous system conditions are still under study. Check out www.theshockwaveacademy.com to learn more!
- Cost and Availability: Access to ESWT may be limited by cost or geographical location. Thankfully, Kinas Medical provides several types of financing and supply the entire U.S. with quality shockwave devices.
Conclusion:
ESWT presents an exciting new approach for treating nervous system diseases, from neuropathy and spasticity to potential applications in neurodegenerative diseases. While more research is needed to establish standardized treatment protocols, the current findings suggest that ESWT could become an essential tool in neurological rehabilitation and pain management.
References:
Study on Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Published in Pain Medicine, this study demonstrated the effectiveness of low-intensity shockwave therapy in alleviating symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy by promoting nerve regeneration and reducing oxidative stress.
Study on Post-Stroke Spasticity: A randomized clinical trial published in the Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine found that ESWT significantly improved spasticity in stroke survivors compared to conventional rehabilitation alone.
Study on Parkinson’s Disease: Published in Neurodegenerative Disease Management, this study suggested that ESWT could improve motor symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease by stimulating dopaminergic pathways and enhancing neuroplasticity.
Study on Neuropathic Pain: A study published in The Clinical Journal of Pain showed that focused shockwave therapy significantly reduced pain scores in patients suffering from chronic low back pain associated with nerve root compression.